 Policy Objectives
Policy Objectives
The administration has four core visions for governance: "Proper Household Waste Management", "Building a High-Quality Environment", "Strengthening Environmental Law Enforcement", and "Preserving Soil and Water Resources". These visions drive ten key areas of focus: optimizing environmental protection facilities, landfill transformation, waste collection, sanitary worker care, enhancing environmental sanitation, promoting quality public restrooms, Salute to the Seas, technological environmental law enforcement, soil and water resource sustainability, and information consolidation. Additionally, 25 measures are implemented, including incineration plant upgrades, ash recycling, waste sorting and fuel conversion, landfill mining and reorganization, environmental protection facility net zero transition, independent waste management solutions for outlying islands, utilizing food waste for energy production, replacing outdated waste collection vehicles, wastewater treatment, environmental sanitation quality enhancement, public restroom maintenance, sanitary worker care, disaster recovery preparation and dispatch, Salute to the Seas promotion, smart fencing systems, enhanced environmental impact assessment supervision, digitalized auditing, prosecutors-police-environmentalist alliance, improved technician auditing practices, regional governance of law enforcement and supervision, reinforced soil and water regulation, site restoration and improvement, remediation technology optimization, soil and water pollution prevention, sustainable soil pollution fund management, information consolidation and cybersecurity promotion, and international cooperation, aiming to create a clean, safe, and sustainable living environment for future generations.
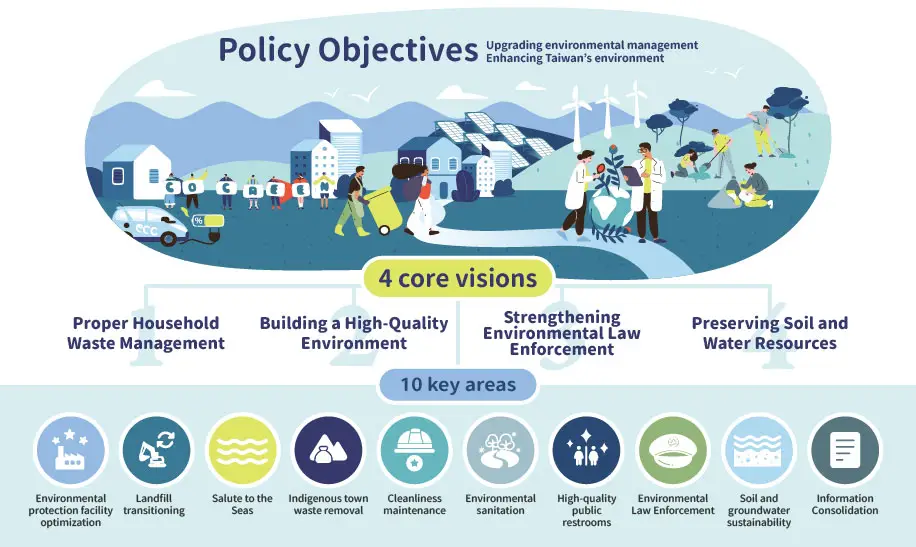
The Environmental Management Administration (EMA) is committed to upgrading incineration facilities, mining and reorganizing landfills, and establishing a landfill safety monitoring center to ensure more efficient and safer waste management. By promoting the recycling of ash and the conversion of waste into fuel, resources are reused through landfill mining, which also creates more usable space while ensuring safe landfill operations. Efforts also include promoting independent waste management solutions for outlying islands, utilizing food waste for energy production, and replacing outdated waste collection vehicles to support the net-zero transition of environmental facilities, thereby enhancing the efficiency of household waste management.
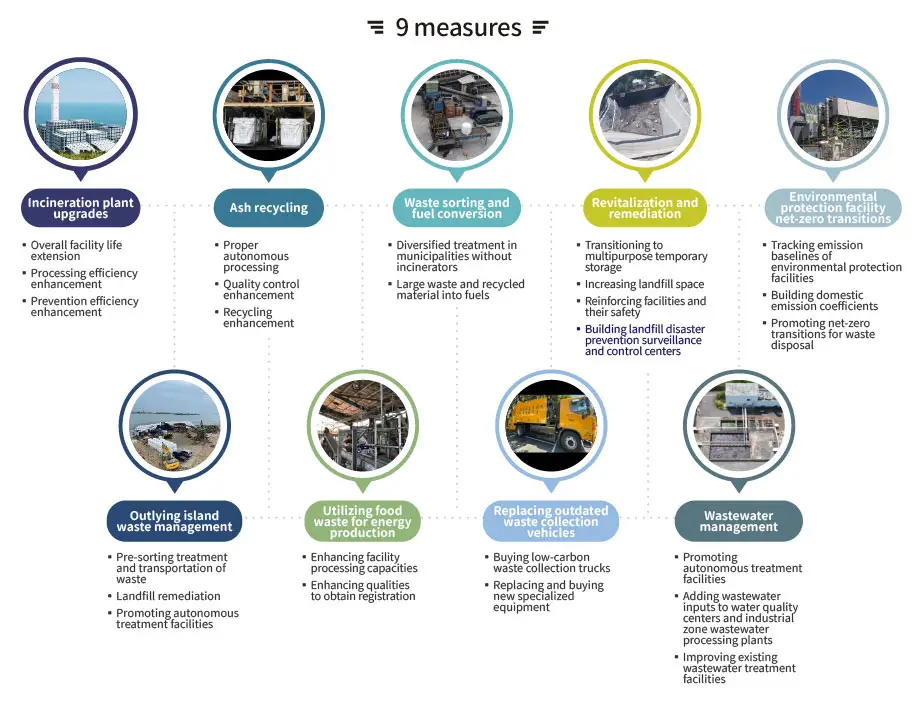
Through five major measures, the administration strives to create a clean, healthy living environment. The measures include enhancing environmental sanitation quality, public restroom maintenance, sanitary worker care, promoting disaster recovery dispatch, and Salute to the Seas coastal cleaning. To improve public restroom management, inventory, inspection and an incentive system are implemented, while safety and care for sanitary workers are also reinforced, and training and occupational safety measures promoted. The administration also actively assists local governments with post-disaster environmental recovery, ensuring quick response through field supervision and dispatch. Key initiatives also focus on dengue fever prevention and coastal cleanup, removing mosquito breeding sources and maintaining the cleanliness of coastlines and rivers.
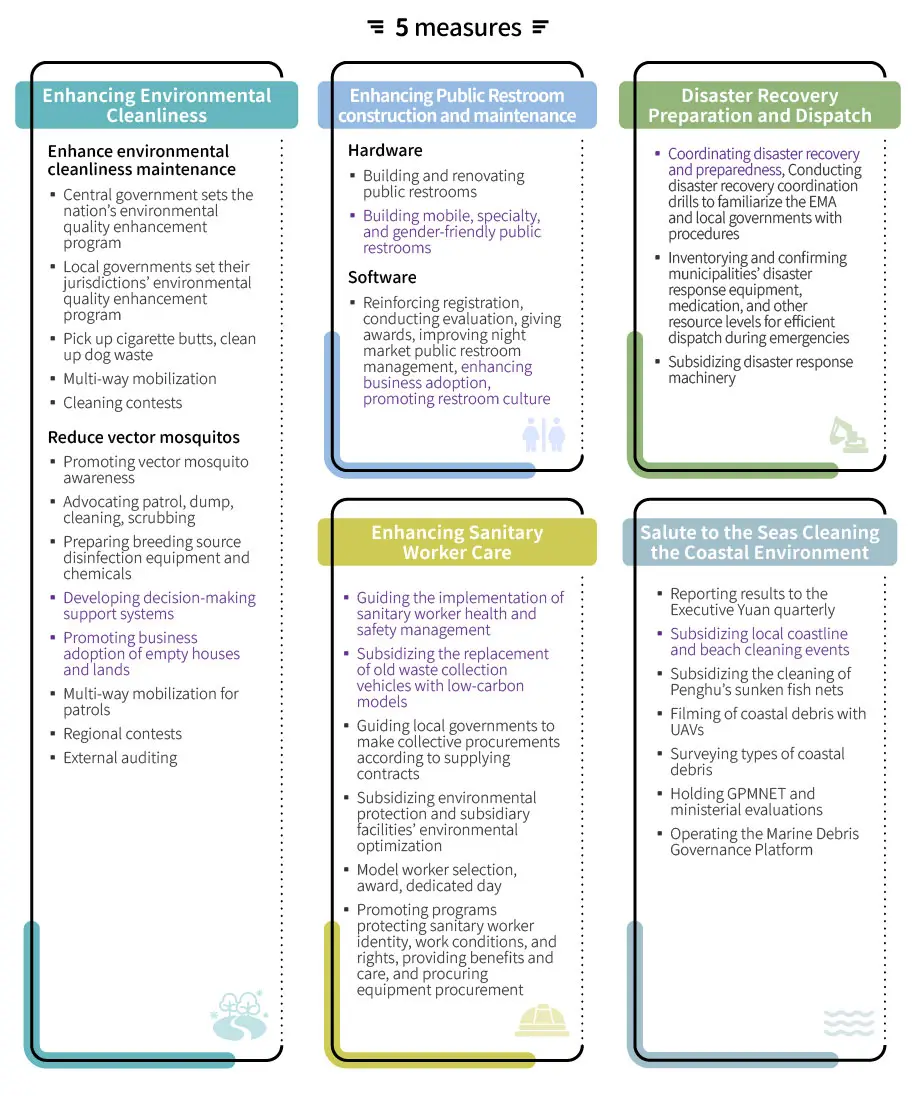
To uphold environmental justice, the administration promotes "remote enforcement" and digitalized audits, integrating diverse information to improve law enforcement effectiveness. Through remote monitoring mechanisms, the administration rigorously oversees development projects to ensure compliance with environmental commitments. Interdisciplinary alliances between prosecutors, police, and environmental authorities strengthen collaborative efforts to combat environmental crime and protect environmental justice. The smart fencing system is central to technological law enforcement, using smart detection to identify and prevent illegal pollution activities promptly. The technician auditing system combines professional expertise with technology to enhance compliance rates among businesses. This series of innovative measures realizes environmental protection and regional governance, as well as promotes pollution prevention, supporting sustainability.
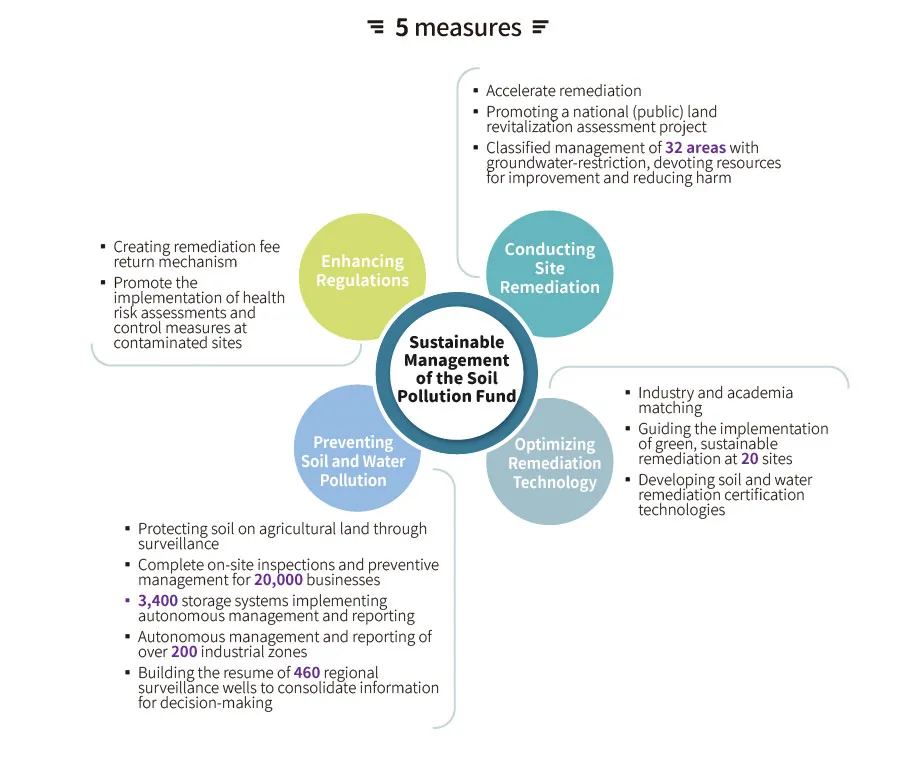
To ensure the sustainable use of soil and groundwater resources, the administration is committed to preventing soil and water contamination, improving the quality of investigations and management, and accelerating the remediation of contaminated sites. For different types of contaminated sites, the administration conducts health risk assessments and implements control measures. Additionally, the administration promotes green remediation and the reuse of contaminated sites, fosters technological innovation, and facilitates international cooperation. Through the management of the Soil and Groundwater Pollution Remediation Fund, the administration ensures the fund's sustainable operation, thereby guaranteeing the continued progress of soil and water pollution prevention and remediation efforts in the future.
- Data Source: Division of General Planning
- Publish Date: 2025-02-21
- Update Date: 2025-08-28
