 Environmental Crime Investigation
Environmental Crime Investigation
Environmental crime typically refers to violations of environmental protection laws and regulations that cause environmental pollution, ecological damage, or resource waste. These may include illegal emissions of pollutants or unlawful dumping of waste. The purpose of investigating environmental crimes is to protect the environment and prevent harm to human health resulting from environmental damage. Law enforcement activities to address environmental crimes include monitoring, investigation, evidence collection, and prosecution, ensuring the effective implementation of environmental laws and the achievement of environmental protection.
Interdisciplinary alliance to combat environmental crimeThe government, from central to local levels, actively collaborates across departments to tackle environmental crime. Since 2011, prosecution, police, and environmental protection agencies, including the Ministry of Justice, the National Police Agency of the Ministry of the Interior, and Ministry of Environment have established a collaborative platform, regularly inviting prosecutors from various regions to join advisory meetings, sharing experiences in investigating environmental crime and developing investigation strategies. These efforts enable environmental, prosecutorial, police, and tax authorities to work more effectively together, continuously protecting the environment and from illegal activities.

To enhance the investigative capabilities and law enforcement efficiency of environmental protection inspectors, the Environmental Management Administration (EMA) has invited experts and scholars from various fields, including prosecutors, police officers, environmental engineers, lawyers, professors, and accountants, to participate in environmental crime case studies and experience exchanges. The EMA also organizes relevant training courses and conferences to help inspectors improve their professional knowledge, refine investigative techniques, and learn to use technological tools. These efforts continually enhance pollution investigation techniques, strengthen interdisciplinary collaboration capabilities, and ensure effective environmental protection.
Effective Evidence Collection and Enhanced Law Enforcement Efficiency
With increasingly complex environmental crimes and pollution cases, advanced technological tools are used to monitor and investigate effectively. For example, by analyzing meteorological conditions, wind direction, wind speed, and air quality data from sensors, probable sources of air pollution can be identified. Drones equipped with night-vision infrared thermal imagers, infrared gas imagers, 3D optical radar, as well as high-position surveillance cameras are also deployed to monitor pollution emissions.
For water pollution, remote water quality monitors are placed in key wastewater discharge areas. Inspectors enter factories for auditing during periods when odorous pollution is likely to occur.
With the aid of technological tools, real-time monitoring of environmental conditions is made possible, reducing manpower and time costs, minimizing risks to inspectors, and effectively gathering evidence of environmental crimes. This boosts law enforcement efficiency and prevents pollution from increasing.
In recent years, environmental crime has become more organized, systematic, professional, and technological, often transcending administrative regions and complicating investigations. With the growth of big data and technological equipment, traditional law enforcement methods are no longer sufficient; technology must be leveraged to increase efficiency.
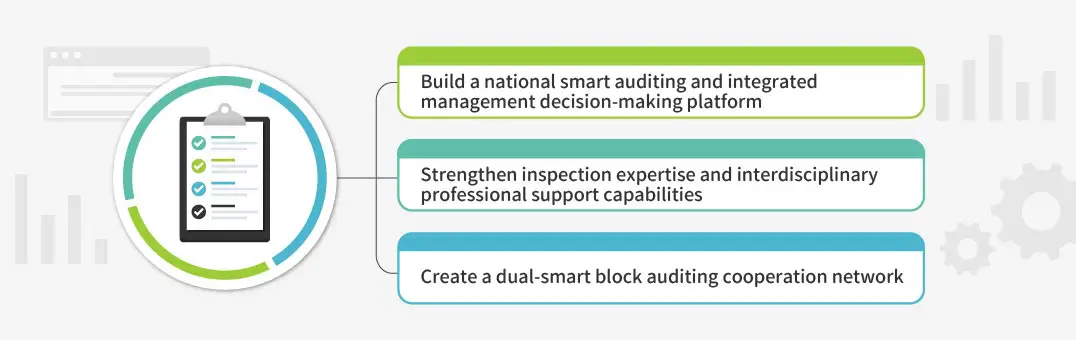
In response, we proposed to the Executive Yuan the "Plan to Prevent Environmental Crime and Implement Smart Enforcement Law for a Green Homeland." This plan includes establishing a "National Smart Auditing and Consolidated Management Decision-Making Platform," enhancing specialized auditing skills and cross-sector support capacities, and creating a dual-smart section auditing collaboration network.
By integrating historical data, remote monitoring, and artificial intelligence, illegal activities can be identified more effectively, helping law enforcement officers detect anomalies early on. Meanwhile, subsidies are provided to enhance local law enforcement officers' interdisciplinary knowledge and skills, increase law enforcement efficiency, and an interdisciplinary alliance for law enforcement addresses major pollution or environmental crime cases.
As society enters the digital era, environmental law enforcement must advance by embracing "remote law enforcement" and adopting a forward-thinking approach in planning overall environmental improvement strategies. In terms of environmental management, this means shifting from "pollution control" to "preventive management." Specifically, the most important change is going from reactive to proactive, moving from passive response to proactive, systematic handling of environmental problems.
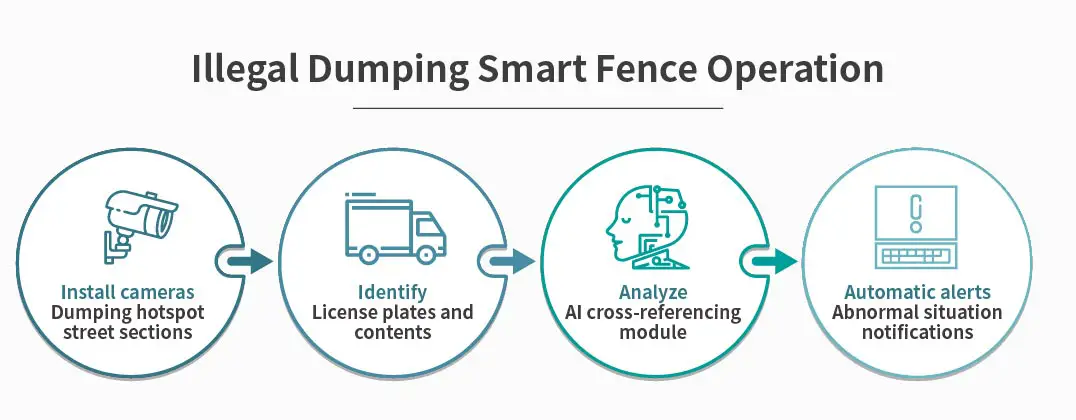
To better prevent the spread of air, water, and waste pollution, we plan to install remote monitoring devices and sensors at key locations in pollution hotspots, creating a web-like network that monitors potential pollution situations. For example: at air pollution hotspots, tiered air sensors are installed according to the location and types of pollutants, allowing for immediate detection of pollution; for water pollution hotspots, water quality sensors are placed at channel nodes or upstream and downstream outlets near monitoring hotspots, enabling continuous water quality tracking; for illegal waste disposal, waste disposal vehicles are monitored in parallel, while license plate recognition systems are installed in disposal hotspots and key roadways to quickly identify unusual disposal activities.
This system not only helps with the early detection of environmental issues but also effectively helps prevent the spread of pollution, leading to better environmental protection.
A collaborative smart auditing network is established between central and local governments, synchronizing all information so that relevant agencies may quickly track and act according to regulations. This significantly enhances environmental quality management and law enforcement efficiency.
ConclusionIn the face of increasingly complex environmental crimes and pollution types, the administration effectively combats environmental crime, enforces environmental regulations, and ensures a high quality of the environment through the interdisciplinary work between prosecutors, police, and environmental authorities, utilizing technological tools, and developing smart fence monitoring for environmental pollution.
- Data Source: Division of Environmental Enforcement
- Publish Date: 2024-08-27
- Update Date: 2025-06-05

 Related Topics
Related Topics



